Simple Infrastructure Design We’ll Create This Time
When constructing infrastructure on AWS, clicking through the console from the browser every time often resulted in missing or incorrect settings in security groups and route tables, which was troublesome.
Therefore, this time we’ll use a tool called Terraform that builds the infrastructure environment just by writing and executing code, automating the construction.
First, let’s look at the completed diagram.
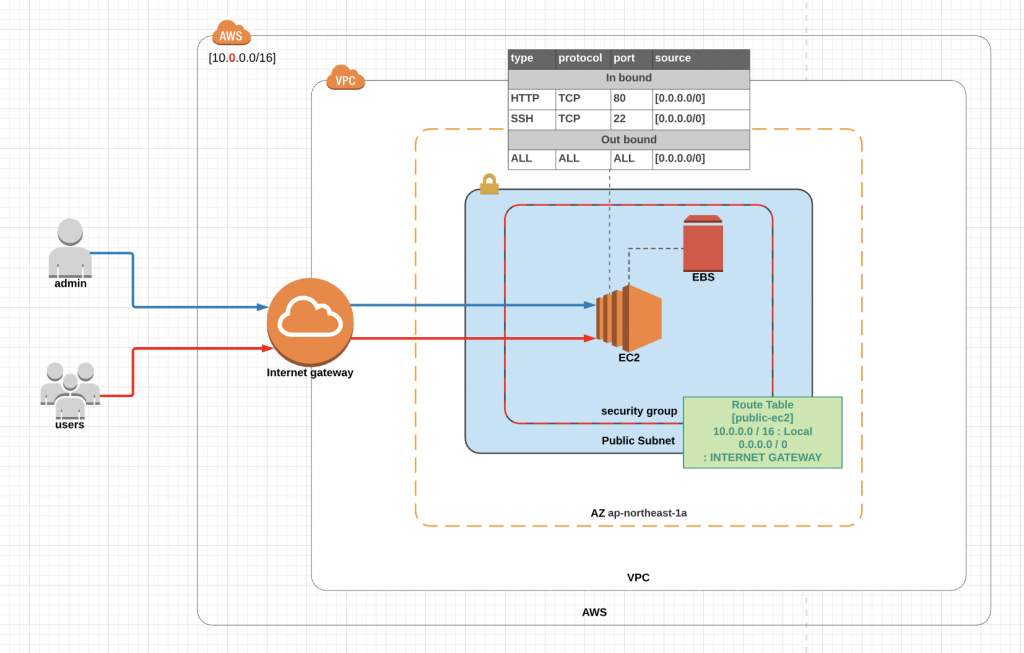
Like this, we’ll create the simplest design possible with just EC2 on VPC.
What is Terraform
Let me briefly explain what Terraform is.
It’s a tool developed by HashiCorp, the company that developed Vagrant, and according to the official HP:
HashiCorp Terraform enables you to safely and predictably create, change, and improve infrastructure. It is an open source tool that codifies APIs into declarative configuration files that can be shared amongst team members, treated as code, edited, reviewed, and versioned. https://www.terraform.io/
In other words, Terraform is an open source tool that can safely and predictably create/change/improve infrastructure design and treat it as code.

Using this, you can build infrastructure environments from code and easily delete them with a single command.
When constructing from a browser, you have to click through settings from the console, and when you want to destroy the built environment, you have to delete each one individually, which is a disadvantage. Terraform solves these issues.
Since you can reuse once-designed infrastructure structures, it’s a very convenient tool once you can use it.
Infrastructure Construction Steps
Now, let’s proceed with infrastructure construction using Terraform step by step.
Installing Terraform
This time, using a Mac,
brew install terraform
You can quickly install Terraform with this.
To check if Terraform was installed successfully,
terraform version
Let’s check if this command works. Now you’re ready.
Preparation: Obtaining API Key
To use Terraform, you need an API key to handle AWS externally.
API key acquisition can be done for each IAM user, so please create one in advance.
From the created IAM user page’s credentials in the browser, please create an access key.
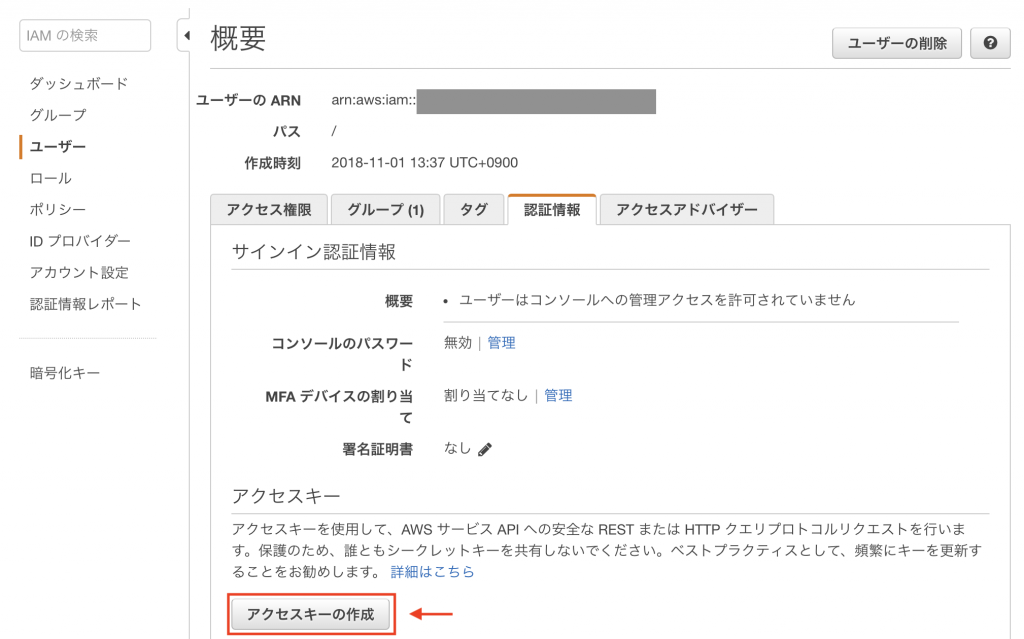
This creates an access key ID and secret key ID. The secret key ID is only displayed temporarily, so make sure to note it down properly.
Files to Create
Now, let’s list the files needed to design a simple VPC+EC2 environment.
- terraform.tfvars
- aws.tf
- vpc.tf
- ec2.tf
tf files and tfvars files that set terraform variables are automatically read when placed in the same directory.
Therefore, file names can be set freely and files don’t need to be separated, but this time I’m separating files considering readability and versatility.
terraform.tfvars
With the extension “.tfvars”, you can define variables to use when using terraform.
While variables can be defined in “.tf” too, environment variables that you don’t want to upload to Git like this file will be defined here.
aws_access_key = "XXXXX" // your access key
aws_secret_key = "XXXXX" // your secret key
aws_region = "ap-northeast-1"
server_name = "test-terraform"
key_name = "XXXXXXXX" // key pair
network_part_ip = "0"
aws_zone = "ap-northeast-1a"
amazon_linux_2_ami = "ami-0d7ed3ddb85b521a6"
Like this, set the access key and secret key you obtained earlier.
This table shows what each variable means.
| Variable name | Content |
|---|---|
| aws_access_key | Access key ID |
| aws_secret_key | Secret key ID |
| aws_region | Region name |
| server_name | Server name (※Used when naming EC2 etc.) |
| key_name | Key pair name (※Already created this time) |
| network_part_ip | Network part IP (if creating VPC with 10.2.0.0/16, this value is 2) |
| aws_zone | Availability zone name |
| amazon_linux_2_ami | amazon linux 2 image ID |
To make identification easier when conducting multiple infrastructure designs in the same account, tags are used to name security groups and route tables, so server_name is pre-defined as a name prefix to use at that time.
When launching EC2, set the key pair necessary for EC2 access.
While you can create new ones from Terraform, this time we’ll use an existing key pair. Therefore, write the key pair name you’ll use in key_name.
If you don’t have a key pair, create one from the console by creating a key pair.
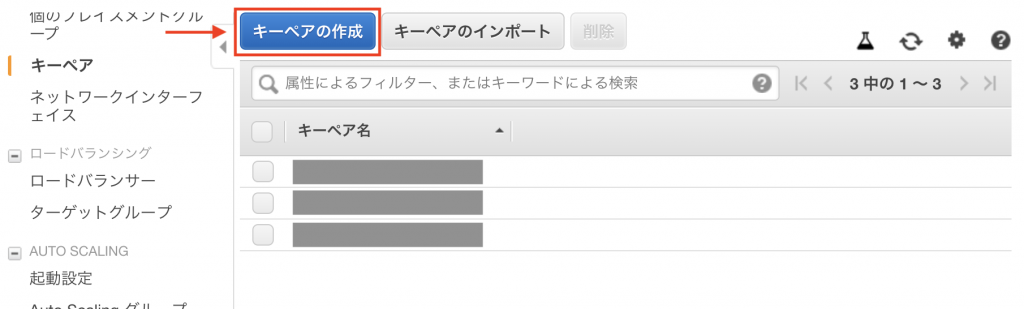
Here, download the private key and save it in the ~/.ssh directory of the PC performing SSH connection.
aws.tf
This file manages variable declarations and API initialization. Now let’s look at the aws.tf code.
// use tfvars
variable "aws_access_key" {}
variable "aws_secret_key" {}
variable "server_name" {}
variable "aws_region" {}
variable "key_name" {}
variable "aws_zone" {}
variable "network_part_ip" {}
variable "amazon_linux_2_ami" {}
// init
provider "aws" {
access_key = "${var.aws_access_key}"
secret_key = "${var.aws_secret_key}"
region = "${var.aws_region}"
}
In the code written here
variable "XXXXX" {}
This part declares that variables defined in terraform.tfvars will be used.
After this, they can be called as follows:
"${var.XXXXX}"
The provider needs to be set with the access key, secret key, and region.
vpc.tf
Next, let’s configure the VPC.
// vpc
resource "aws_vpc" "vpc" {
cidr_block = "10.${var.network_part_ip}.0.0/16"
enable_dns_support = true
enable_dns_hostnames = true
tags {
Name = "${var.server_name}-vpc"
}
}
// internet gateway
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "igw" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.vpc.id}"
tags {
Name = "${var.server_name}-igw"
}
}
In terraform, settings for all resources like EC2, RDS, security groups, VPC are written like this:
resource "method name" "variable name" {
// Write detailed settings here
}
For what methods are available, check the official documentation.
VPC detailed settings are summarized below.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| cidr_block | CIDR block to use in VPC (e.g., 10.0.0.0/16) |
| enable_dns_support | Whether DNS resolution is supported for the VPC |
| enable_dns_hostnames | Whether instances launched in the VPC get public DNS hostnames |
| tags | Tags (can set Name) |
Next, internet gateway detailed settings.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| vpc_id | VPC to attach internet gateway to |
| tags | Tags (can set Name) |
ec2.tf
Next, EC2 settings.
// subnet
resource "aws_subnet" "public-subnet" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.vpc.id}"
cidr_block = "10.${var.network_part_ip}.1.0/24"
availability_zone = "${var.aws_zone}"
tags {
Name = "${var.server_name}-public-subnet"
}
}
// route table
resource "aws_route_table" "public-route" {
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.vpc.id}"
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = "${aws_internet_gateway.igw.id}"
}
tags {
Name = "${var.server_name}-public-route"
}
}
// route table association
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public-ec2-route" {
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.public-subnet.id}"
route_table_id = "${aws_route_table.public-route.id}"
}
// security group
resource "aws_security_group" "public-ec2-sg" {
name = "public-ec2-sg" // group name
description = "for public-ec2"
vpc_id = "${aws_vpc.vpc.id}"
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
// self = true
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 443
to_port = 443
protocol = "tcp"
// self = true
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
ingress {
from_port = 22
to_port = 22
protocol = "tcp"
// self = true
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
tags {
Name = "${var.server_name}-public-ec2-sg"
}
}
// ec2
resource "aws_instance" "public-ec2" {
ami = "${var.amazon_linux_2_ami}"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
vpc_security_group_ids = ["${aws_security_group.public-ec2-sg.id}"]
subnet_id = "${aws_subnet.public-subnet.id}"
associate_public_ip_address = false
key_name = "${var.key_name}"
root_block_device = {
volume_type = "gp2"
volume_size = "8" // GB
delete_on_termination = true
}
tags {
Name = "${var.server_name}-public-ec2"
}
}
To build EC2, you must build these 3 things:
Subnet
Route table
Security group
First, the subnet.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| vpc_id | VPC to use |
| cidr_block | CIDR block (e.g., 10.0.1.0/24) |
| availability_zone | Availability zone to use |
| tags | Tags (can set Name) |
Next, route table.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| vpc_id | VPC to use |
| route > cidr_block | CIDR block (e.g., 0.0.0.0/0) |
| route > gateway_id | Internet gateway to use |
| tags | Tags (can set Name) |
You need to associate route table and subnet, so configure with aws_route_table_association.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| subnet_id | Subnet to associate |
| route_table_id | Route table to associate |
And security group.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| name | Group name |
| description | Comment |
| vpc_id | VPC to use |
| ingress | Inbound settings (detailed below) |
| egress | Outbound settings (detailed below) |
| tags | Tags (can set Name) |
Both ingress and egress use the same keys to set inbound and outbound.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| to_port | First port (which port to which port to accept) |
| from_port | Last port (which port to which port to accept) |
| protocol | Protocol (e.g., TCP, SSH) |
| cidr_blocks | CIDR block (e.g., 0.0.0.0/16) |
Finally, EC2 settings.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| ami | Image to use |
| instance_type | Instance type (e.g., t2.micro) |
| vpc_security_group_ids | Security group to use |
| subnet_id | Subnet to use |
| associate_public_ip_address | Associate with public IP |
| key_name | Key pair name |
| root_block_device | EBS settings (detailed below) |
| tags | Tags (can set Name) |
Set initial EBS capacity etc. with root_block_device as follows.
| Key | Content |
|---|---|
| volume_type | Volume type (e.g., gp2) |
| volume_size | Volume size (unit is GB) |
| delete_on_termination | Delete EBS when EC2 is deleted |
Infrastructure Construction with Terraform Commands
Now all files are created.
Finally, let’s perform infrastructure construction from the created code with terraform commands.
First, move to the directory where tf files are saved and execute this command.
terraform init
Then initialization is performed, resulting in something like this:
Initializing provider plugins... - Checking for available provider plugins on https://releases.hashicorp.com... - Downloading plugin for provider "aws" (1.58.0)... The following providers do not have any version constraints in configuration, so the latest version was installed. To prevent automatic upgrades to new major versions that may contain breaking changes, it is recommended to add version = "..." constraints to the corresponding provider blocks in configuration, with the constraint strings suggested below. * provider.aws: version = "~> 1.58"
Terraform has been successfully initialized!
You may now begin working with Terraform. Try running "terraform plan" to see
any changes that are required for your infrastructure. All Terraform commands
should now work.
If you ever set or change modules or backend configuration for Terraform,
rerun this command to reinitialize your working directory. If you forget, other
commands will detect it and remind you to do so if necessary.
This completes initial setup for terraform.
If you suddenly do “terraform plan” command for dry run without doing terraform init,
Plugin reinitialization required. Please run "terraform init".
Reason: Could not satisfy plugin requirements.
Plugins are external binaries that Terraform uses to access and manipulate
resources. The configuration provided requires plugins which can't be located,
don't satisfy the version constraints, or are otherwise incompatible.
1 error(s) occurred:
* provider.aws: no suitable version installed
version requirements: "(any version)"
versions installed: none
Terraform automatically discovers provider requirements from your
configuration, including providers used in child modules. To see the
requirements and constraints from each module, run "terraform providers".
Error: error satisfying plugin requirements
You’ll get an error like this, so be careful.
After initialization is done, after that:
terraform plan
Do a dry run to confirm there are no errors, then:
terraform apply
This builds the environment. Now you can create a VPC+EC2 infrastructure environment.
If you want to delete all of this environment:
terraform destroy
This can delete it. This command is incredibly convenient.
Also, when you want to delete part of the environment:
terraform destroy target=aws_instance.public-ec2
Use the target option like this.
There’s also:
terraform refresh
to apply changes to terraform when you’ve manually modified the environment.
It’s good to check these out.
Summary
This time, we built a super simple VPC+EC2 infrastructure environment using terraform.
Were you able to understand terraform’s basic usage?
With this, you can easily create environments including load balancers, auto scale, RDS, CloudFront, etc., so please try using Terraform.
